陈凯余 1,2,3,4,5李颖 1,2,3,4李政岱 1,2,3,4郭友明 1,2,3,4,*
1 中国科学院自适应光学重点实验室,四川 成都 610209
2 中国科学院光电技术研究所,四川 成都 610209
3 中国科学院大学,北京 100049
4 中国科学院大学电子电气与通信工程学院,北京 100049
5 光场调控科学技术全国重点实验室,四川 成都 610209
无透镜成像系统使用掩模板替代镜头,在降低成本的同时使设备更加轻巧,然而在进行目标识别前需通过计算重建图像,涉及参数调优和计算耗时问题。基于此,提出一种无重建的目标识别方案,直接在无透镜相机拍摄的编码图像上训练网络识别目标,在节约计算资源的同时还提供隐私保护。使用具有相位掩模板和振幅掩模板的无透镜相机,仿真生成MNIST与Fashion MNIST数据集和实采MNIST数据集,然后在这些数据集上训练ResNet-50与Swin_T网络进行目标识别。结果表明,在仿真MNIST、Fashion MNIST和真实MNIST数据集上,所提方案的最高识别准确率达99.51%、92.31%和98.06%,与先重建目标后识别方案的准确率相当,证明所提方案是一种高效的、具有隐私保护的端到端方案,且在两种掩模板和两类常规骨干分类网络上得到了验证。
计算成像 目标识别 深度学习 无透镜成像 激光与光电子学进展
2024, 61(8): 0811008

Youming Guo 1,2,3,4Kele Chen 1,2,3,4,5Jiahui Zhou 1,2,3,4Zhengdai Li 1,2,3,4[ ... ]Changhui Rao 1,2,3,4,*
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 The Key Laboratory on Adaptive Optics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Chengdu 610209, China
2 Institute of Optics and Electronics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Chengdu 610209, China
3 University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China
4 School of Electronic, Electrical and Commutation Engineering, University of Chinese Academy of Science, Beijing 100049, China
5 National Key Laboratory of Optical Field Manipulation Science and Technology, Chengdu 610209, China
Integrating deformable mirrors within the optical train of an adaptive telescope was one of the major innovations in astronomical observation technology, distinguished by its high optical throughput, reduced optical surfaces, and the incorporation of the deformable mirror. Typically, voice-coil actuators are used, which require additional position sensors, internal control electronics, and cooling systems, leading to a very complex structure. Piezoelectric deformable secondary mirror technologies were proposed to overcome these problems. Recently, a high-order piezoelectric deformable secondary mirror has been developed and installed on the 1.8-m telescope at Lijiang Observatory in China to make it an adaptive telescope. The system consists of a 241-actuator piezoelectric deformable secondary mirror, a 192-sub-aperture Shack-Hartmann wavefront sensor, and a multi-core-based real-time controller. The actuator spacing of the PDSM measures 19.3 mm, equivalent to approximately 12.6 cm when mapped onto the primary mirror, significantly less than the voice-coil-based adaptive telescopes such as LBT, Magellan and VLT. As a result, stellar images with Strehl ratios above 0.49 in the R band have been obtained. To our knowledge, these are the highest R band images captured by an adaptive telescope with deformable secondary mirrors. Here, we report the system description and on-sky performance of this adaptive telescope.
adaptive optics deformable secondary mirror visible imaging Opto-Electronic Advances
2023, 6(12): 230039
1 电子科技大学电子科学技术研究院四川成都 611731
2 电子科技大学格拉斯哥学院四川成都 611731
事件句的句法结构有助于语义理解。针对中文领域的事件检测任务, 本文设计了面向句义及句法的事件检测模型(BDD)以增强对事件句的理解能力。以基于来自变压器的双向编码器表示 (BERT)的动态词向量为信息源, 设计基于依存树的长短时记忆网络模型(D-T-LSTM)以融合学习句法结构及上下文语义, 并加入基于依存向量的注意力机制强化对不同句法结构的区分度, 在中文突发事件语料库(CEC)上的实验证明了本文模型的有效性, 精确率、召回率、F1值均靠前, 且 F1值比基准模型提升了 5.4%, 召回率提升了 0.4%。
事件检测 来自变压器的双向编码器表示 基于依存树的长短时记忆网络模型 基于依存向量的注意力机制 event detection Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transfo Dependency-Tree-LSTM(Long Short-Term Memory Networ D-Attention 太赫兹科学与电子信息学报
2023, 21(12): 1464

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 The Key Laboratory on Adaptive Optics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Chengdu 610209, China
2 The Laboratory on Adaptive Optics, Institute of Optics and Electronics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Chengdu 610209, China
3 University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China
Adaptive optics techniques have been developed over the past half century and routinely used in large ground-based telescopes for more than 30 years. Although this technique has already been used in various applications, the basic setup and methods have not changed over the past 40 years. In recent years, with the rapid development of artificial intelligence, adaptive optics will be boosted dramatically. In this paper, the recent advances on almost all aspects of adaptive optics based on machine learning are summarized. The state-of-the-art performance of intelligent adaptive optics are reviewed. The potential advantages and deficiencies of intelligent adaptive optics are also discussed.Adaptive optics techniques have been developed over the past half century and routinely used in large ground-based telescopes for more than 30 years. Although this technique has already been used in various applications, the basic setup and methods have not changed over the past 40 years. In recent years, with the rapid development of artificial intelligence, adaptive optics will be boosted dramatically. In this paper, the recent advances on almost all aspects of adaptive optics based on machine learning are summarized. The state-of-the-art performance of intelligent adaptive optics are reviewed. The potential advantages and deficiencies of intelligent adaptive optics are also discussed.
adaptive optics machine learning deep learning Opto-Electronic Advances
2022, 5(7): 200082
1 中国科学院自适应光学重点实验室, 四川 成都 610209
2 中国科学院光电技术研究所, 四川 成都 610209
3 中国科学院大学, 北京 100049
由于分布式全息孔径成像系统的相干性及振幅扩散函数(ASF)的旁瓣效应,成像分辨率的分析非常困难。将瑞利判据两点间分辨率模型推广为多点间分辨率模型,并根据多点ASF在不同相位分布下的叠加曲线判断观测点与其最邻近点的分辨性能。采用遗传算法将观测点与其最邻近点的谷峰比作为目标函数,通过优化多点间相位分布求得某角间距下的最大谷峰比,当最大谷峰比不大于0.81时,则可以分辨该观测点能与最邻近点。求得任意相位发布下,均满足谷峰比不大于0.81的临界角间距,即可将其视作系统角分辨率。仿真和实验结果表明,该方法能够较准确地分析系统分辨率及等效孔径。
全息 分布式全息孔径成像 振幅扩散函数 旁瓣效应 分辨率 等效孔径 激光与光电子学进展
2021, 58(6): 0609001
1 中国科学院自适应光学重点实验室,四川 成都 610209
2 中国科学院光电技术研究所,四川 成都 610209
3 中国科学院大学,北京 100049
在单位圆的同心孔径圆域内,某些特定Zernike模式具有相关关系,其中具有较强负相关关系的模式组合在一定系数条件下叠加后,一定的同心孔径内的像差会相互抵消,波面变得更加平坦,这称为模式间的共轭性。文中设置了一组畸变波前,用自适应光学系统进行校正得到残差,然后用Zernike多项式对变形镜的校正残差进行了分解,通过分析首次发现在均方误差值较大的残差波前中,低阶、高阶两部分像差间存在着明显的负相关关系,两部分像差的系数会随着变形镜控制信号的调整体现出有规律的变化,并且在一定的系数组合方式下,这两部分像差呈现出共轭性。基于以上研究结果,提出一种控制方法,该方法通过优化变形镜控制电压来调整镜面面型,使得残差中的低阶、高阶两部分像差系数实现最佳匹配,从而降低光瞳同心孔径圆域内的像差均方根值 (RMS),最终实现该孔径范围内系统成像质量的提升。分别针对点目标成像和扩展目标成像进行了仿真,结果表明:该方法相比于传统闭环共轭式校正方法,在面对复杂像差时能够得到质量更好的光学成像,有效扩展传统自适应光学系统的适用范围。这种控制方法在变形镜有较大拟合残差的场合具有很好的应用前景。
共轭组合模型 自适应光学系统 控制方法 conjugate combination model adaptive optical system control method 红外与激光工程
2020, 49(9): 20190534
1 中国科学院自适应光学重点实验室, 四川 成都 610209
2 中国科学院光电技术研究所, 四川 成都 610209
3 中国科学院大学, 北京 100049
采用全模式线性二次高斯控制时,多阶模式扰动模型的辨识以及高维控制矩阵的计算会导致实时处理机的计算负担加重。基于此,提出一种适用于实际自适应光学系统的混合控制方法。该方法联合最优模式增益积分控制和线性二次高斯控制算法,根据模式中是否含有窄带扰动来选择对应模式的控制策略。以云南抚仙湖观测站1 m新真空太阳望远镜中高阶自适应光学系统的实测数据为例,对提出的控制策略进行了验证。结果表明,采用本文提出的混合控制策略,使系统中95.85%的扰动得到有效滤除。该控制方法与全模式使用最优模式增益积分控制的方法相比,不同频率的窄带扰动得到明显抑制;该方法与全模式使用线性二次高斯控制的方法相比,扰动模型的辨识所花费的时间缩短了37.77%,控制运算所花费的时间缩短了73.8%,有利于扰动的实时校正。
自适应光学 最优模式增益积分控制 线性二次高斯控制 扰动 激光与光电子学进展
2020, 57(23): 230101
1 中国科学院自适应光学重点实验室,四川 成都 610209
2 中国科学院光电技术研究所,四川 成都 610209
3 中国科学院大学,北京 100049
对太阳大气进行大视场高分辨力光学成像观测是开展太阳物理、空间天气等基础与应用研究的重要前提。对于地基太阳望远镜而言,为了消除地球大气湍流对光学系统的影响,自适应光学是高分辨力成像观测必备的技术手段,与此同时,为了突破大气非等晕性对传统自适应光学校正视场的限制,近年来多层共轭自适应光学技术等大视场自适应光学得到极大发展。本文首先梳理国外太阳自适应光学系统研制情况,重点介绍国内太阳自适应光学技术发展及应用情况,并进一步介绍了后续大视场太阳自适应光学技术发展情况以及目前所取得的成果。
太阳观测 自适应光学 多层共轭自适应光学 solar observation adaptive optics multi-conjugate adaptive optics
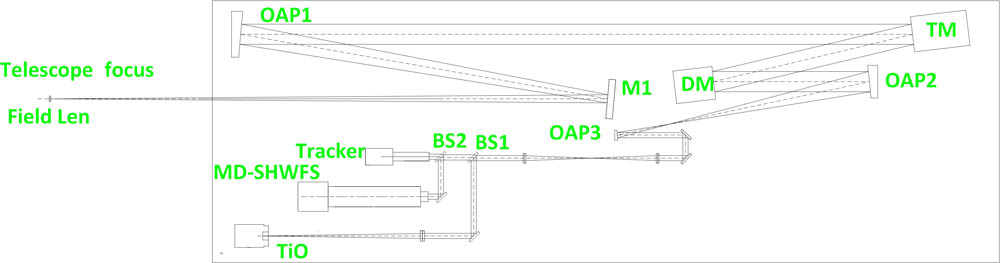
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 The Key Laboratory on Adaptive Optics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Chengdu 610209, China
2 The Laboratory on Adaptive Optics, Institute of Optics and Electronics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Chengdu 610209, China
3 University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China
A prototype of a solar ground-layer adaptive optics (GLAO) system, which consists of a multi-direction correlating Shack–Hartmann wavefront sensor with 30 effective subapertures and about a 1 arcmin field of view (FoV) in each subaperture, a deformable mirror with 151 actuators conjugated to the telescope entrance pupil, and a custom-built real-time controller based on field-programmable gate array and multi-core digital signal processor (DSP), is implemented at the 1 m New Vacuum Solar Telescope at Fuxian Solar Observatory and saw its first light on January 12th, 2016. The on-sky observational results show that the solar image is apparently improved in the whole FoV over 1 arcmin with the GLAO correction.
010.1080 Active or adoptive optics 110.1080 Active or adoptive optics Chinese Optics Letters
2016, 14(10): 100102

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 The Key Laboratory on Adaptive Optics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Chengdu 610209, China
2 The Laboratory on Adaptive Optics, Institute of Optics and Electronics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Chengdu 610209, China
3 University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China
A second generation solar adaptive optics (AO) system is built and installed at the 1-m New Vacuum Solar Telescope (NVST) of the Fuxian Solar Observatory (FSO) in 2015. The AO high-order correction system consists of a 151-element deformable mirror (DM), a correlating Shack–Hartmann (SH) wavefront sensor (WFS) with a 3500 Hz frame rate, and a real-time controller. The system saw first light on Mar. 16, 2015. The simultaneous high-resolution photosphere and chromosphere images with AO are obtained. The on-sky observational results show that the contrast and resolution of the images are apparently improved after the wavefront correction by AO.
010.1080 Active or adoptive optics 110.1080 Active or adoptive optics 110.0115 Imaging through turbulent media Chinese Optics Letters
2015, 13(12): 120101





